UX Test II
Jun.-Prof. Dr. Mark Hall
Sommersemester 2019
Themen
- Planung
- Leistungsmetriken
- Verhalten / Physiologische Metriken
- Benutzerfeedback
- Durchführung
- Analyse
Planung
- Was ist das Ziel des Tests?
- Was für eine Interaktion wird getestet?
- In welchem Umfeld wird getestet?
- Wer sind die Benutzer/innen?
Leistungsmetriken
- Erfolg
- Zeit
- Fehler
- Effizienz
- Lernbarkeit
Verhalten / Physiologische Metriken
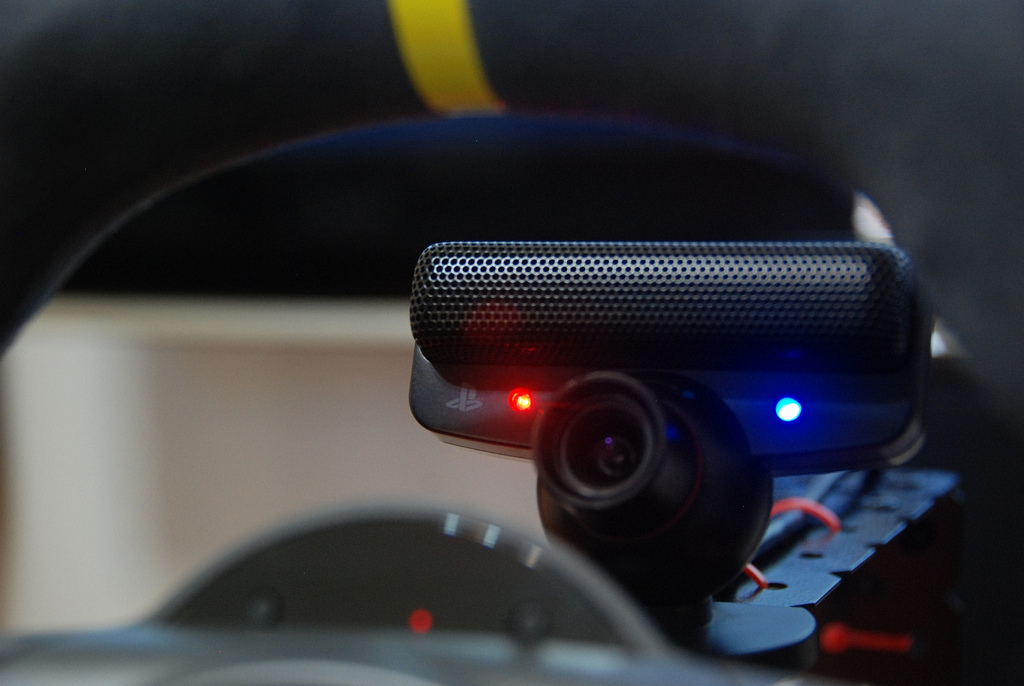
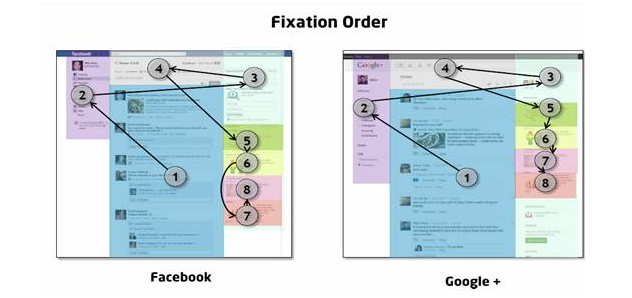
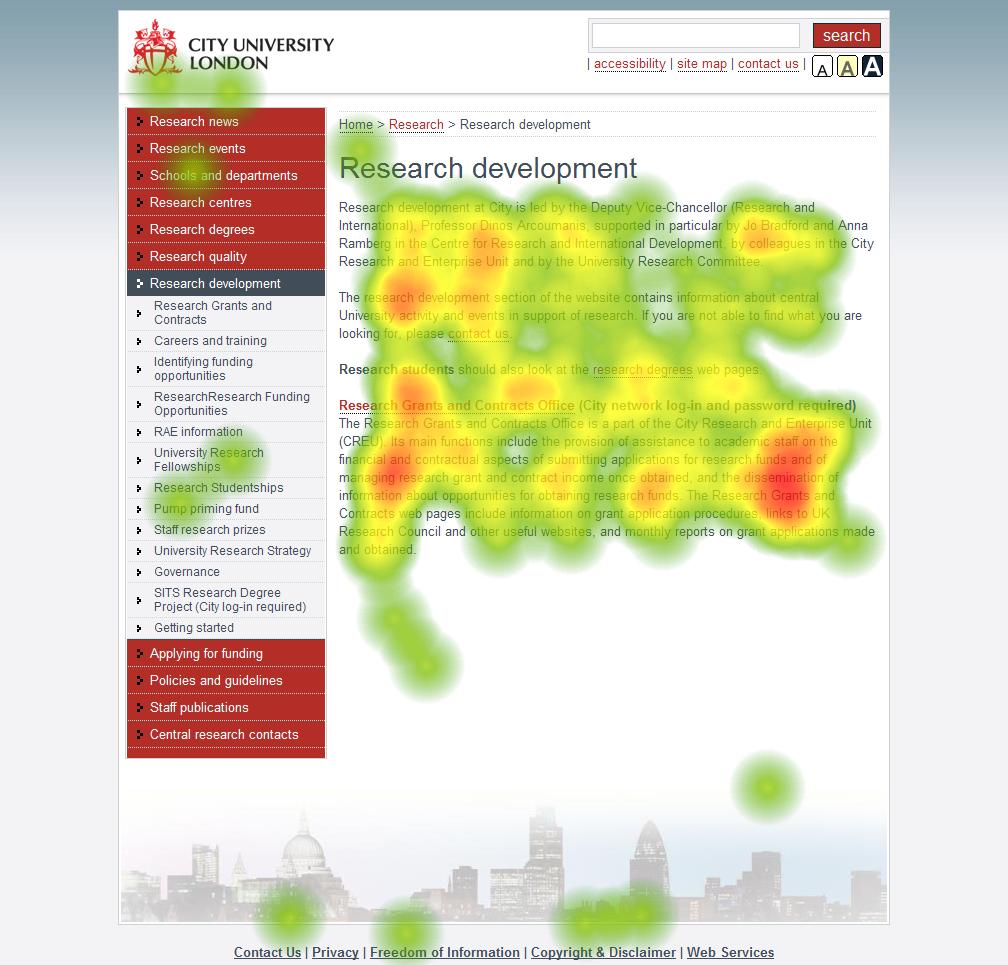
- Eye Tracking
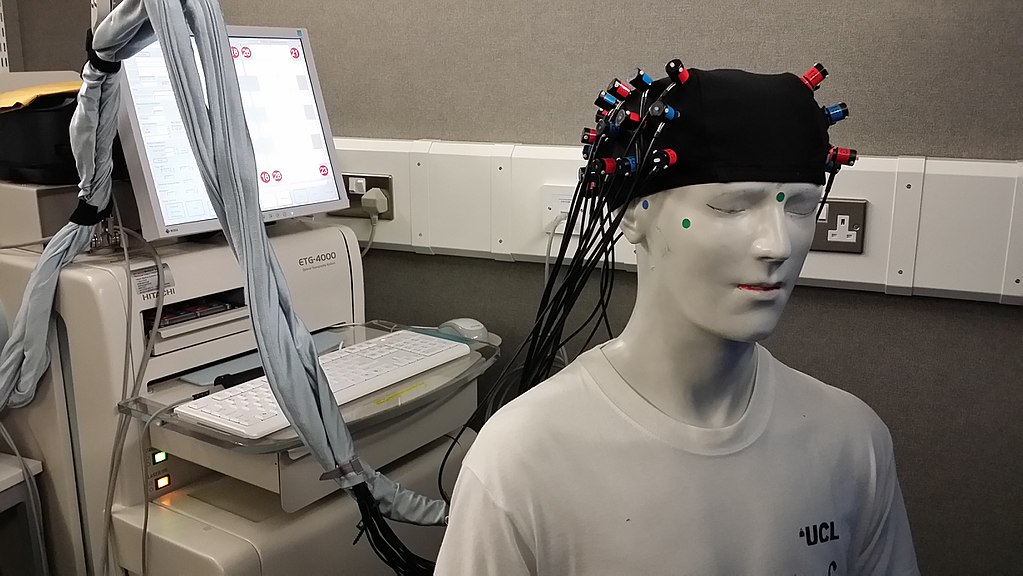
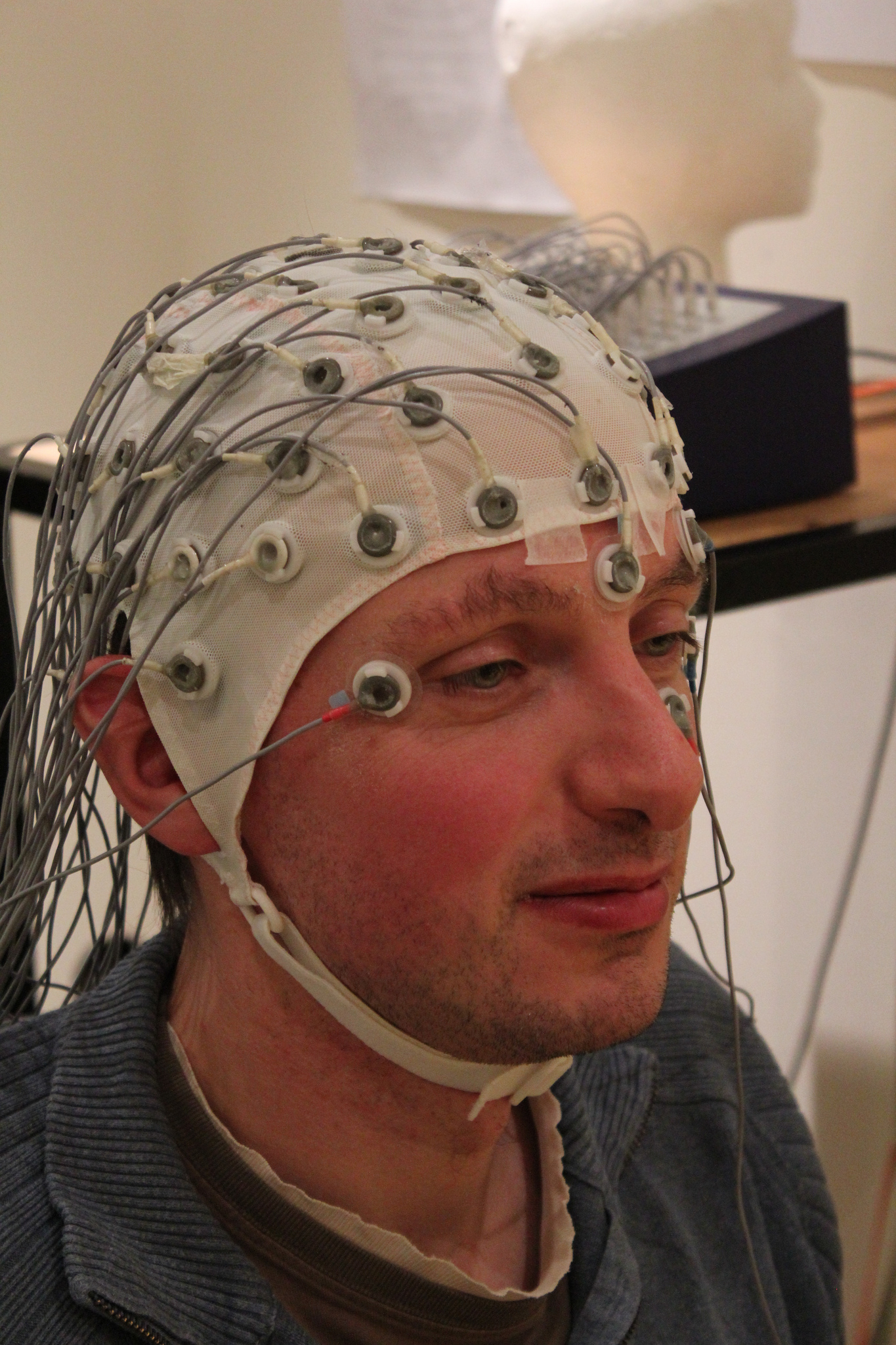
- fNIRS
- EEG
- Emotionsensors
Eye Tracking
fNIRS / ECG
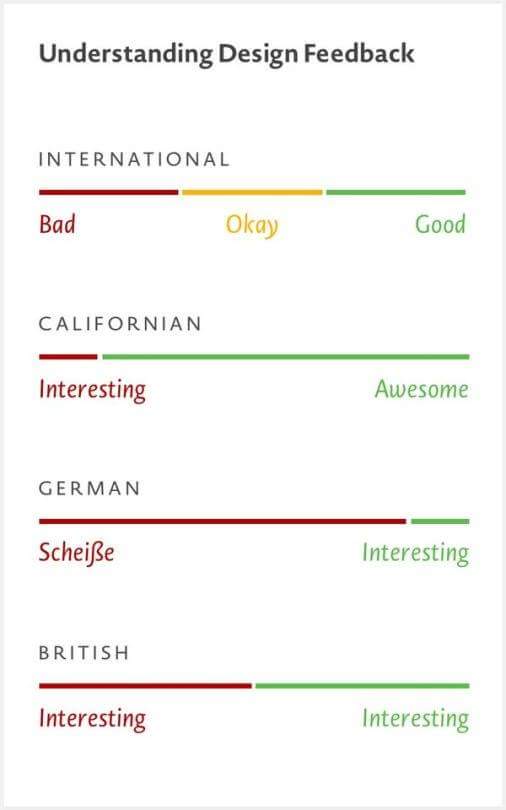
Testerfeedback
- Demographie
- Hintergrund
- Likert-like
- Semantische Differentiale
- System Usability Scale (SUS)
- NASA-TLX (Task Load indeX)
- User Engagement Score (UES)
- Qualitatives Feedback
Demographie / Hintergrund
- Gender
- Alter
- Bildung
- Sprachkenntnisse
- Task-spezifisches Vorwissen
- Kontextuelles Vorwissen
Likert-like Fragen
| Stimme nicht zu | 2 | 3 | 4 | Stimme zu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ich habe etwas neues gelernt | |||||
| Das außergewöhnliche Interface hat mich begeistert |
Semantische Differentiale
| Das Interface war | hässlich | attraktiv | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Das Interface war | schlecht | einfach |
System Usability Score
| Strongly disagree | ... | Strongly agree | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I found the system unnecessarily complex | |||
| I thought the system was easy to use | |||
| I think that I would need the support of a technical person to be able to use this system | |||
| I think that I would like to use this system frequently | |||
| I found the various functions in this system were well integrated | |||
| I thought there was too much inconsistency in this system | |||
| I would imagine that most people would learn to use this system very quickly | |||
| I found the system very cumbersome to use | |||
| I felt very confident using the system | |||
| I needed to learn a lot of things before I could get going with this system |
NASA-TLX

User Engagement Score
| Kategorie | Strongly disagree | ... | Strongly agree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA-S | I lost myself in this experience. | |||
| FA-S | The time I spent using Application X just slipped away. | |||
| FA-S | I was absorbed in this experience. | |||
| PU-S | I felt frustrated while using this Application X. | |||
| PU-S | Using this Application X was taxing. | |||
| PU-S | I found this Application X confusing to use. |
User Engagement Score
| Kategorie | Strongly disagree | ... | Strongly agree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE-S | This Application X was attractive. | |||
| AE-S | This Application X was aesthetically appealing. | |||
| AE-S | This Application X appealed to my senses. | |||
| RW-S | Using Application X was worthwhile. | |||
| RW-S | My experience was rewarding. | |||
| RW-S | I felt interested in this experience. |
Feedback
Studientypen
- Moderierte (klassische) Tests
- Remote (online) Tests
- Umfragen
Latin Square
| Interface 1 | Interface 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Aktivität 1 | A | B |
| Aktivität 2 | C | D |
Latin Square
| A | B | C | D |
| A | B | D | C |
| A | C | B | D |
| ... | |||
Latin Square
| A | C |
| C | A |
| B | D |
| D | B |
Studienkategorien
- Transaktion
- Produktvergleich
- Regelmäßige Verwendung eines Produkts
- Navigationstest
- Sichtbarkeit von UI Elementen
- Problemsuche
- Maximierung der Benutzerfreundlichkeit
- Eine positive UX ermöglichen
- Testen kleiner Veränderungen
- Designvergleiche
Durchführung
- Pre-Experiment
- Pre-Task 1
- Task 1
- Post-Task 1
- Pre-Task 2
- Task 2
- Post-Task 2
- Post-Experiment
Durchführung
- Bildschirm/Videoaufnahme und Annotation
- Talk aloud während des Experiments
- Talk aloud nach dem Experiment
- Diskussion der Annotierten Events
Analyse
- Beschreibende Statistik
- Vergleichende Statistik
- Faktoranalyse
- Textanalyse
Literatur
- Tullis, T. and Albert, B. (2013). Measuring the User Experience. Morgan Kaufmann.
- Krug, S. (2014). Don't Make Me Think Revisited. New Riders.